7 Arten von Dünnschichten (Beschichtungen), die in optischen Linsen verwendet werden.



When coating an optical lens, the design of the coating as well as the lens will change depending on the various product applications. Let’s take a look at some of the typical coatings used for optical lenses.
(1) AR coating (Anti-Reflection coat)
This coat is used to increase the amount of light transmitted through the lens by lowering the amount of reflected light on the substrate (lens) surface.
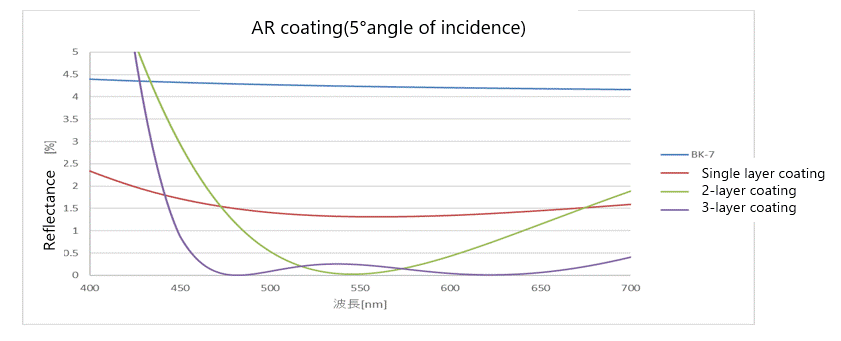


Let’s call the substrate BK-7.
(BK-7/optical glass – used as a substrate for mirrors, beam splitters, and various vapor deposition filters, in addition to lenses and prisms)
The reflectivity is reduced by adding one to three layers of dielectric film to the substrate.
The single-layer coating reduces the overall reflectivity. (4.2% to about 1.3%)
2-layer coating lowers the reflectance of only certain wavelengths. (Around 550nm)
The 3-layer coating lowers the reflectance of the entire wavelength. (450 to 700nm)
Therefore, it is necessary to select the type of coating depending on the product application.
(2) Half Mirror Coat (HMT)
Half Mirror Coat is a coating that separates the amount of transmitted light and the amount of reflected light. When the light is divided 50:50, it is called half mirror coat.
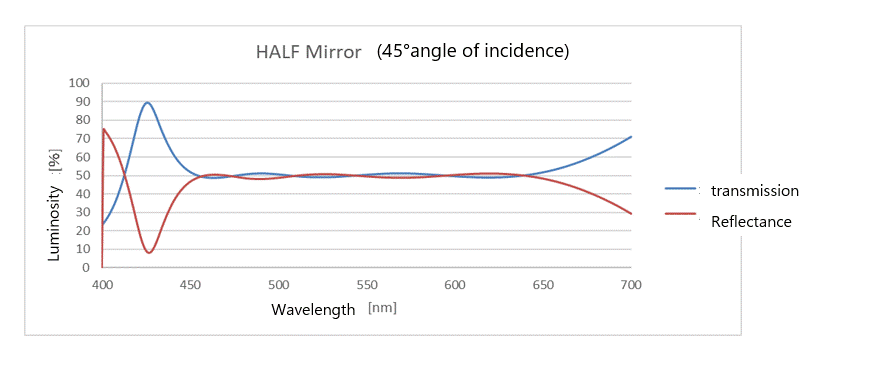


Depending on the product standard, it is possible to design membranes with various optical separations, such as 80:20 or 60:40, to achieve detailed separation settings.
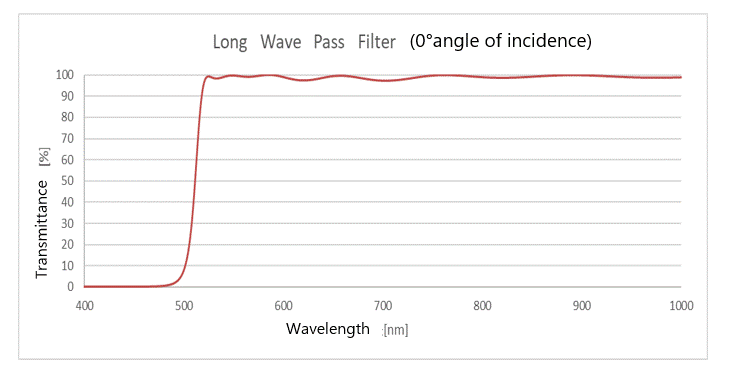
(3) Long Wave Pass Filter (LWF)
A coating that blocks the amount of light transmitted at short wavelengths and allows the amount of light transmitted at long wavelengths to pass through.


(4) Short Wave Pass Filter
This is a coating that transmits the amount of transmitted light on the short wavelength side and blocks the amount of transmitted light on the long wavelength side.
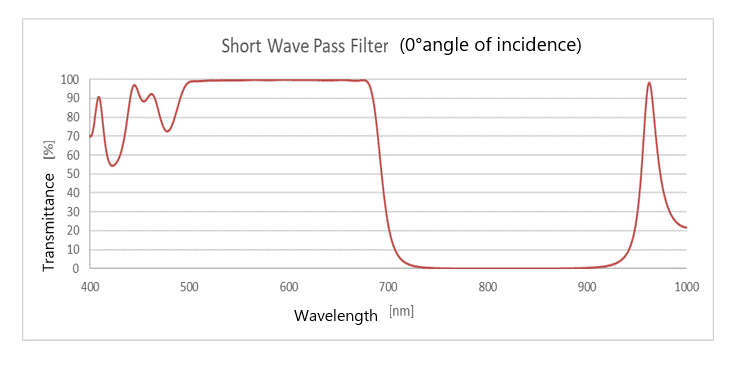


When the wavelength is more than 700nm (∴ Transmits the amount of visible light, and blocks the amount of light in the infrared region)
Also known as IR Cut Filter (InfraRed Cut Filter).
(5) Band pass filter (Band Pass Filter)
This is a coating that transmits light only in a certain range of wavelengths and blocks light in other wavelengths.
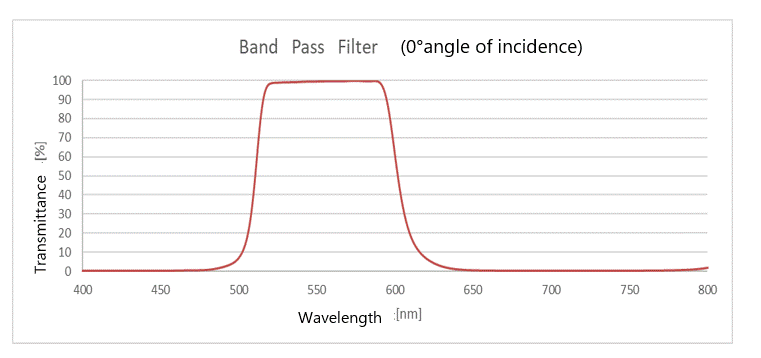


Depending on the product standard, the wavelength range can be further narrowed by designing the membrane to pass through.
(6) Dielectric mirror
This is a coating that uses a dielectric as the deposition material to increase the amount of reflected light by limiting it to a certain range of wavelengths.
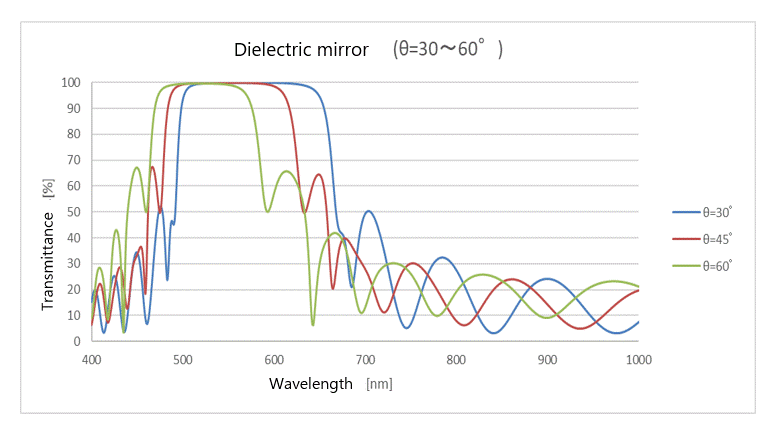


It is characterized by changes in the spectral characteristic waveform as the angle of incidence changes. Dielectric mirrors are often selected when durability testing of the product itself is required.
(7) Metallic mirror (aluminum mirror)
This coating uses aluminum (metal) as the vapor deposition material to increase the amount of reflected light over the entire wavelength range.
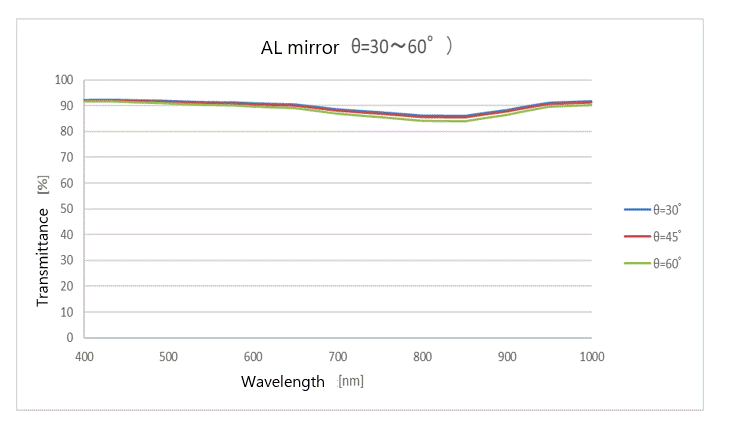


By using a metallic film, it is possible to obtain a high amount of reflected light over the entire wavelength, but it is not possible to obtain a high amount of reflected light at a specific wavelength at the dielectric film level. However, changing the angle of arrival does not affect the change in the amount of reflected light.
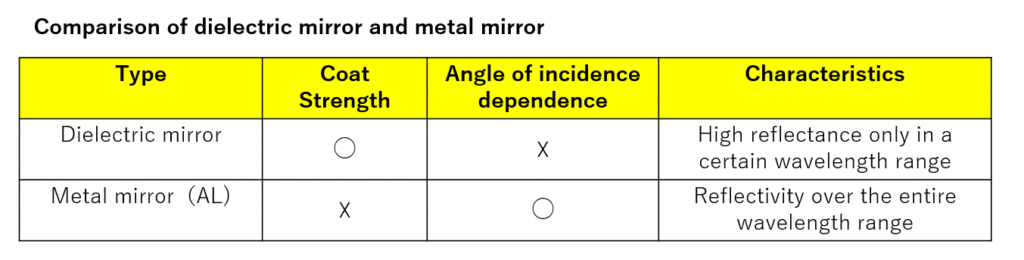


Whether to use dielectric mirror coating or metal mirror coating should be selected according to the product specifications.
For all your optical design needs, contact Optical Design Technology Navi!
TOYOTEC Corporation, the company that operates Optical Design Technology Navi, is a comprehensive optomechatronics optical manufacturer that designs and develops products from scratch to meet customer needs, and provides integrated support from design to commercialization.
I want a product like this… “Is it possible to do this with lenses? Optical Design Technology Navi, a group of optical design professionals, is the answer to these questions. If you have any questions about optical design, please feel free to contact us at Optical Design Technology Navigator.
 JP Phone: 0533-85-3000
JP Phone: 0533-85-3000


-340x220.jpg)